Subsections
MIDI ports provide an abstraction layer for your MIDI hardware and
synthesizers (which can be both software and hardware synthesizers),
and other MIDI applications. Port are numbered. In order to produce
sound, each MIDI track is assigned to exactly one MIDI port, to which
the MIDI events are then sent.
The advantage of this abstraction layer is that if your system changes,
for example you change MIDI hardware, then you need only modify the
ports instead of all the tracks using those ports. This is similar
to the audio input and output track abstraction to the outside world.
In the midi/softsynth configuration menu, you must map the port numbers
to the actual devices (by selecting ALSA or jack midi ports, or synth
plugins).
Try left-clicking on the "Ports" column of some MIDI track.
If you use a soft synth, right-clicking the Ports column of the synth
or any track using the synth lets you launch the synth's GUI.
Figure 2.13:
Midi configuration window
|
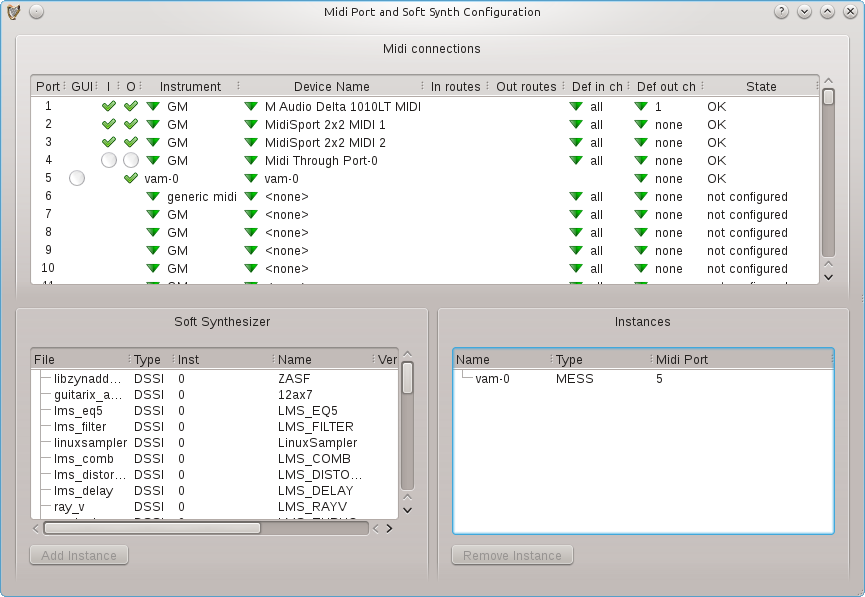 |
- GUI:
- For synthesizer devices, indicates if a gui is available
and if it is showing. Click to show.
- I:
- If present, the port can accept MIDI input. Click to
enable or disable it.
- O:
- If present, the port can send MIDI output. Click to enable
or disable it.
- Instrument:
- Selects the instrument to be used when MIDI is
played through the port.
- Device name:
- Selects or creates a MIDI device assigned to the
port. These can be Jack MIDI devices or ALSA MIDI devices (if ALSA is
enabled), or soft synthesizers. Jack MIDI devices are created by selecting
Create Jack Device from the Device name drop-down menu. Jack MIDI devices
can be renamed as you wish by clicking the device name. Soft synthesizers
are created by clicking in the soft synthesizer list and then Add
Instance. Or you can simply create a new synthesizer track from the
arranger track list, or even the mixer menus.
- In and Out routes:
- These are for Jack MIDI devices, they are
the routes to and from available Jack MIDI ports. Jack may provide
different alias names for these ports, you can select which alias
is shown.
- Default in channels:
- Auto-connect these port channels to
new midi or drum tracks.
- Default out channel:
- Auto-connect new midi or drum tracks
to this channel on the port.
- State:
- Indicates the state of the port including any errors
opening it.
Plugins can usually process an arbitrarily small (or large) amount
of samples. If some plugin control value changes continously, to provide
ideal listening experience, MusE would need to call the plugin 44100
times a second, asking for one single value at a time. With the minimum
control period setting, the user can force MusE to ask the plugin for
at least N values. Setting this value to 64 would in this situation
make MusE call the plugin
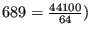 times a second,
asking for 64 values at a time. While doing this will reduce accuracy
of control changes, it may also reduce CPU usage, because calling
the plugin more often, requesting smaller chunks, is more expensive
than calling it seldomly, requesting larger chunks.
If you have no performance problems, or if you want to do the final
downmix of your project, set this to a low value. If you're experiencing
performance problems, increasing this value might help.
times a second,
asking for 64 values at a time. While doing this will reduce accuracy
of control changes, it may also reduce CPU usage, because calling
the plugin more often, requesting smaller chunks, is more expensive
than calling it seldomly, requesting larger chunks.
If you have no performance problems, or if you want to do the final
downmix of your project, set this to a low value. If you're experiencing
performance problems, increasing this value might help.